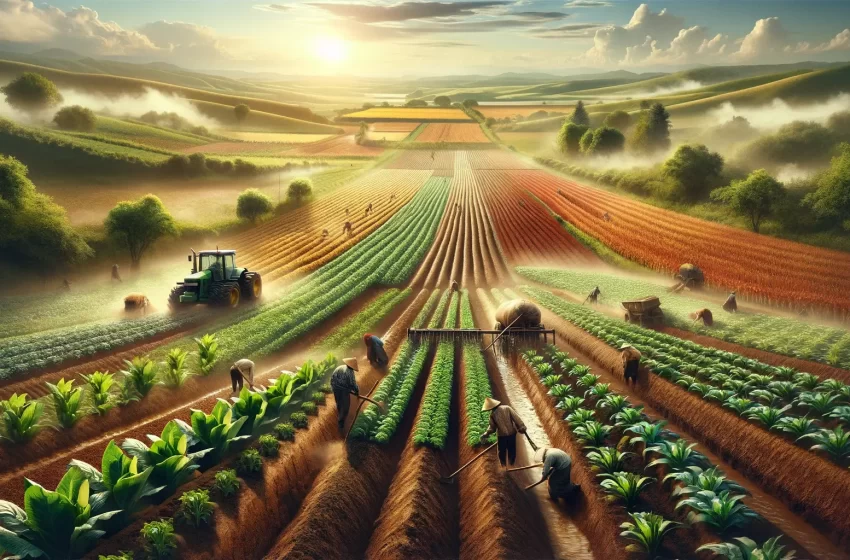
Agriculture, integral to society globally, shapes our world, often overlooked amidst advancing technology and urbanization. Yet, as climate change, food insecurity, and economic disparity escalate, its significance grows clearer daily – not just as an occupation or industry, but as the cornerstone of human civilization, profoundly influencing its future.
Cultivating land for food, fiber, or fuel, agriculture melds art and science. Historically, it’s been pivotal, offering sustenance and livelihoods to billions. Even with industrialization and technological progress on its way out of its infancy phase, however, its core principles remained constant: nurturing soil nutrients while drawing upon nature to power development through interdependencies between people and nature.
One of the remarkable qualities of agriculture is its resilience. Farmers continue to adapt and innovate despite challenges such as climate variability, pests and diseases, resource constraints, and land ownership constraints to increase the yield and sustainability of their land. From ancient farming techniques to cutting-edge agrotech solutions developed over centuries – agriculturalists’ ingenuity has long been essential in feeding humanity across various environments and helping humanity prosper as a species.
As our global population approaches 9 billion by 2050, pressure on agricultural systems increases exponentially. To meet food demands for such an increasing population requires not just increasing yields but doing it sustainably and fairly; agriculture holds the key to meeting this challenge with innovations ranging from precision farming and genetic engineering to agroecology and regenerative agriculture as solutions.
Technological innovations play a pivotal role in increasing agricultural productivity and efficiency. Precision agriculture enabled by drones, sensors, and data analytics allows farmers to maximize inputs like water, fertilizers, and pesticides while simultaneously minimizing waste and environmental impact. Meanwhile, biotechnological developments like genetically modified crops provide opportunities to strengthen crop resilience, nutritional content and yield potential to bolster food security against climate change and other risks.
Sustainable Agriculture
While productivity remains of great concern in agriculture, sustainable practices aim to achieve more than mere output; environmental stewardship, social equality, and economic viability all play crucial roles. Sustainable agricultural practices aim to minimize adverse effects on ecosystems while conserving natural resources, increasing biodiversity while maintaining fair wages and working conditions for farmworkers – this applies both organic farming, and agroforestry as well as rotational grazing or no-till cultivation techniques – that support agricultural sustainability.
Agriculture holds great potential to combat climate change by sequestering carbon in soils, lowering greenhouse gas emissions, and supporting renewable energy sources like biofuels. By adopting eco-friendly principles and adopting climate-smart practices, farmers can play a significant role in both adapting to and mitigating its effects – contributing greatly towards long-term efforts toward environmental sustainability and resilience.
Fostering Innovation and Collaboration
Unlocking agriculture’s full potential requires not only technological innovation but also collaboration among various stakeholders – government bodies, research institutes, NGOs, and private enterprises all play a part in providing an enabling environment for innovation and entrepreneurship to flourish in agriculture. Investment in agricultural research services and extension, access to finance markets and policies, and supportive regulations all are vitally important in enabling farmers and rural communities to thrive in an ever-evolving globalized society.
Digital technologies and data-driven insights have transformed agriculture, providing real-time monitoring, decision-making, and market access. Utilizing platforms such as mobile apps, blockchain or satellite imaging allows farmers to overcome information asymmetries while improving supply chain transparency as well as traceability and food safety standards – thus creating value for producers, consumers, and society as a whole.
At this pivotal juncture of human civilization’s evolution, agriculture stands as one of its linchpins and its impact can no longer be understated. From feeding an ever-increasing global population to maintaining environmental balance on Earth, agriculture holds key solutions for some of humanity’s biggest issues – all while offering generations to come a brighter and more prosperous future through innovation, sustainability, and collaboration.